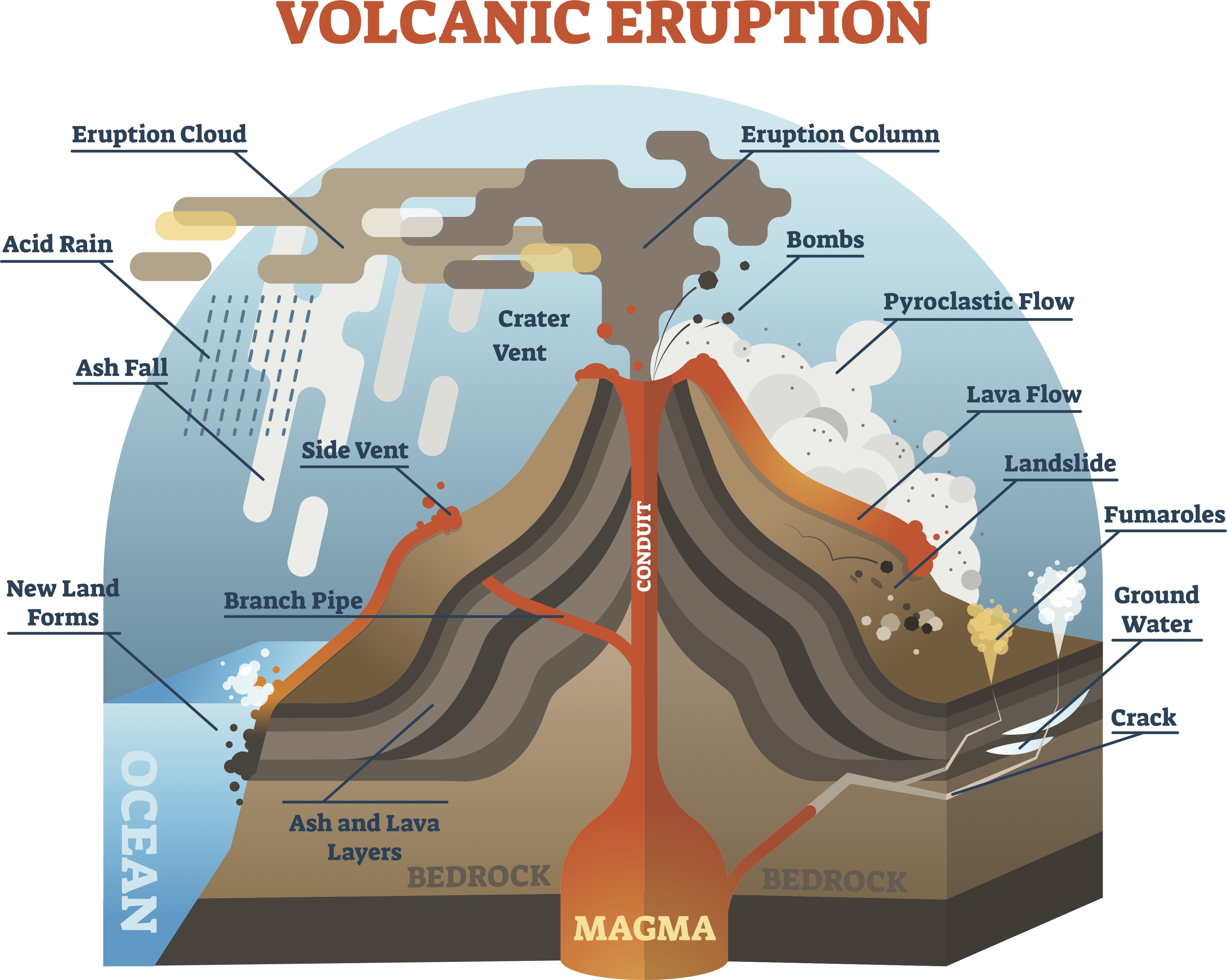
12+ Volcanic Eruption Diagram Robhosking Diagram
A volcano is a geological structure that results from the accumulation of magma (molten rock), ash, and gases beneath the Earth's surface. When pressure builds up within the Earth's crust, it can lead to the eruption of this material through vents or openings, creating a variety of landforms.
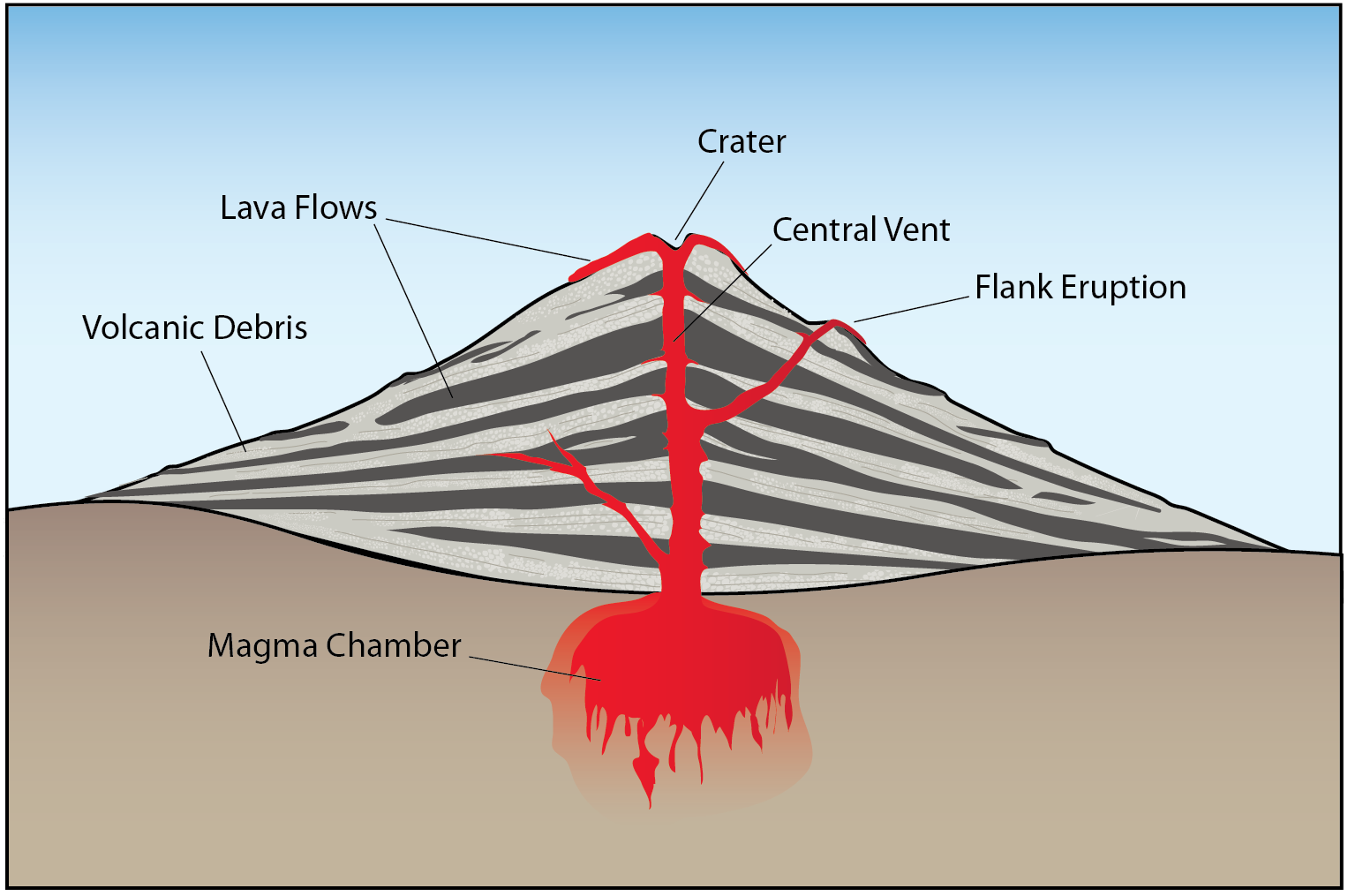
Anatomy Of A Volcano anatomy diagram source
A volcano is an opening in a planet or moon's crust through which molten rock, hot gases, and other materials erupt. Volcanoes often form a hill or mountain as layers of rock and ash build up from repeated eruptions. Volcanoes are classified as active, dormant, or extinct. Active volcanoes have a recent history of eruptions; they are likely.
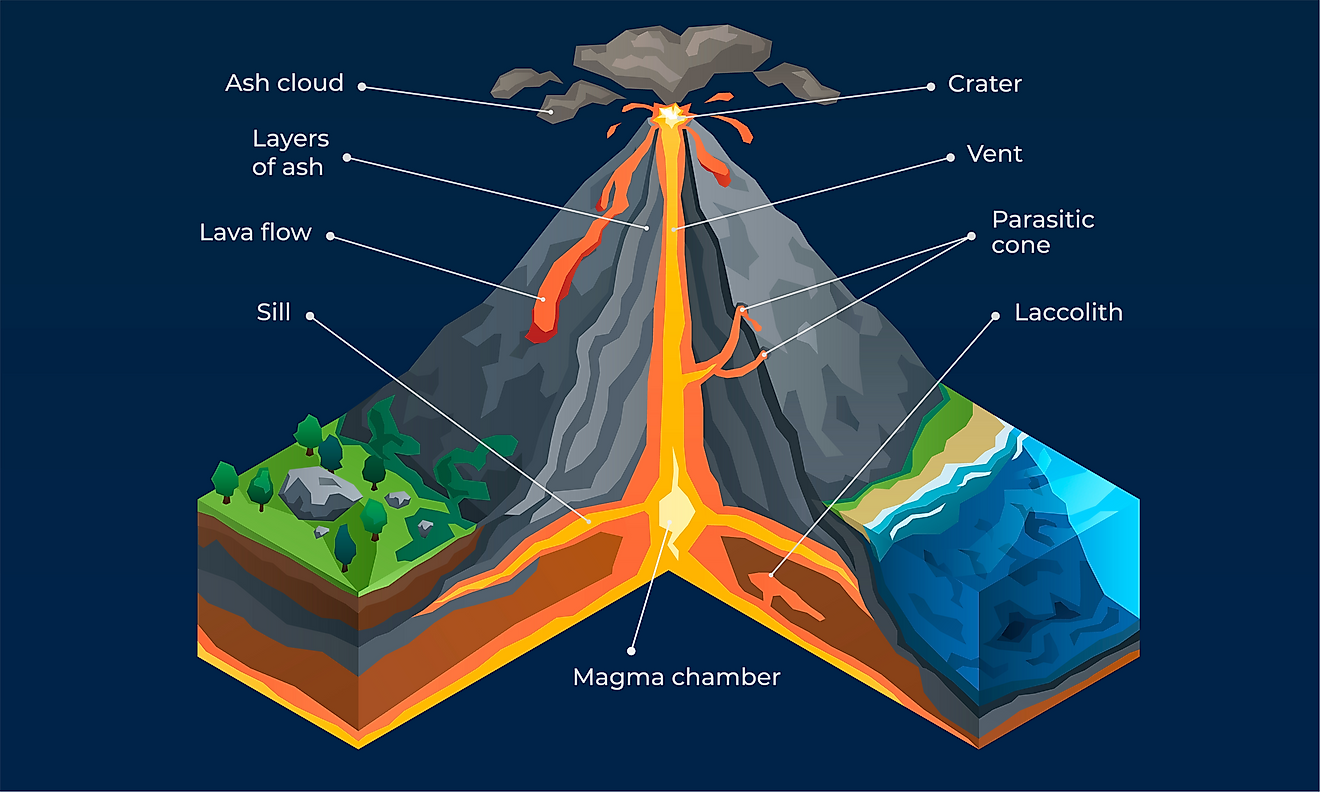
What Happens When A Volcano Erupts? WorldAtlas
The familiar cone-shape of many volcanoes are an indication of this, the point at which ash, rock and lava ejected during an eruption fall back to Earth around the vent to form a protrusion..
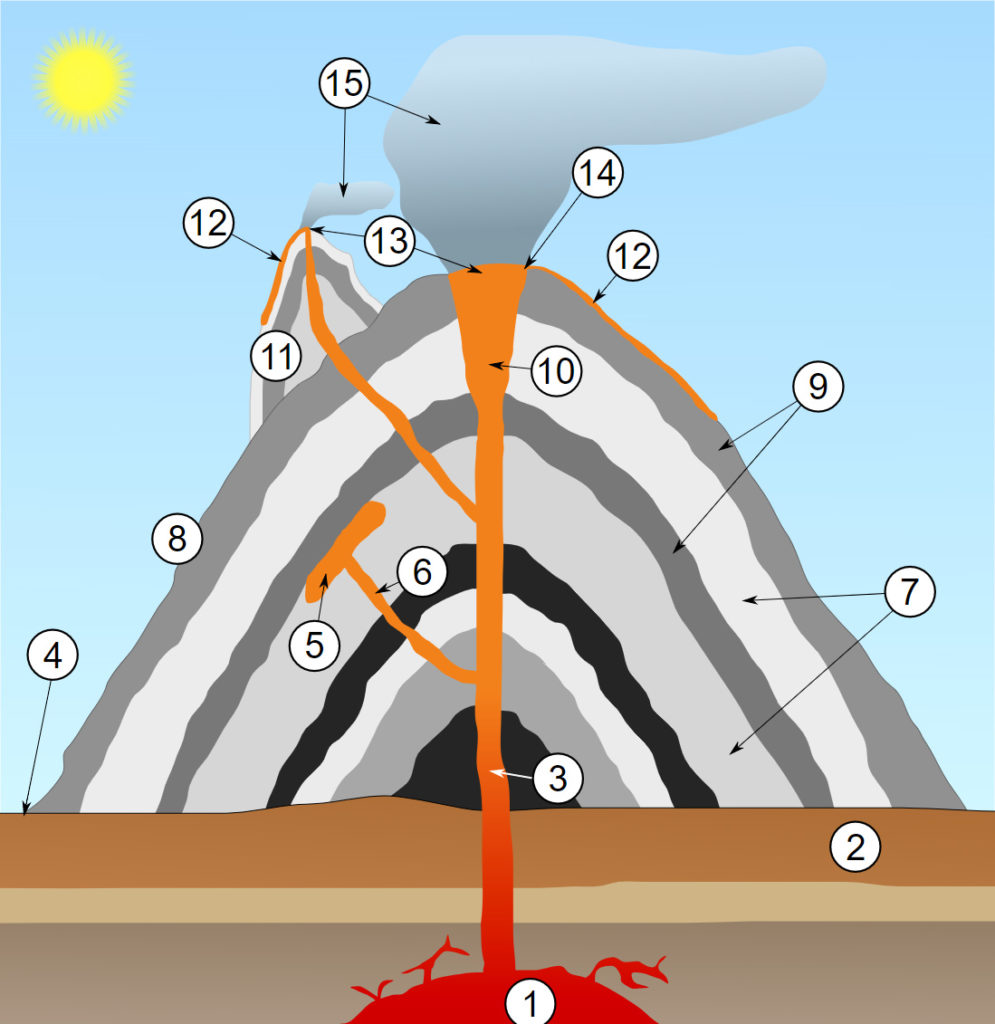
Partes de un volcán Conociendo la anatomía de un volcán NeoTeo
Volcanoes have long intrigued the world. They are scary and fascinating. Learn the parts of a typical volcano in this informative video. This is part 2 in a.

Potter's Geography Features of a Volcano
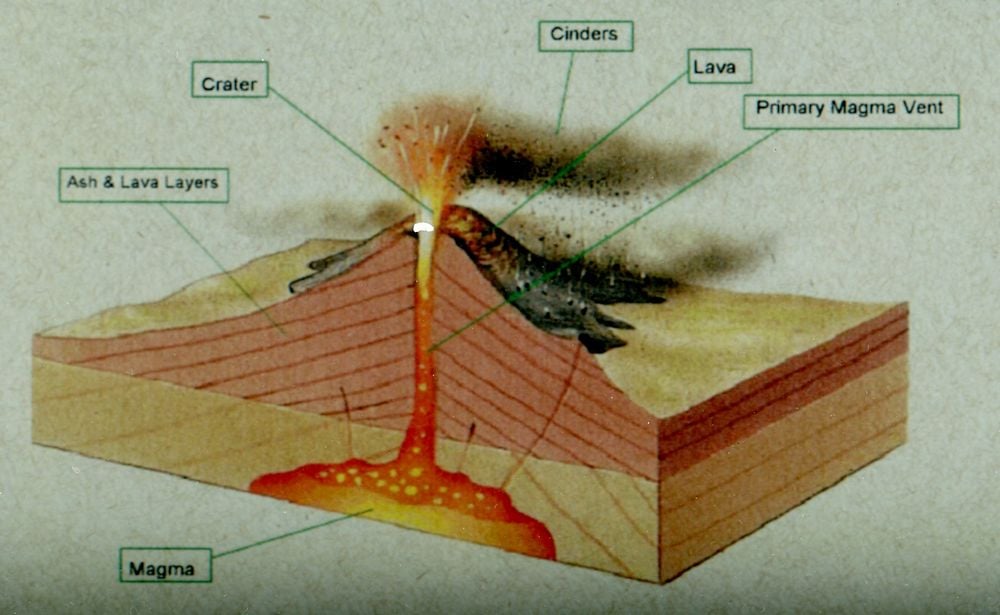
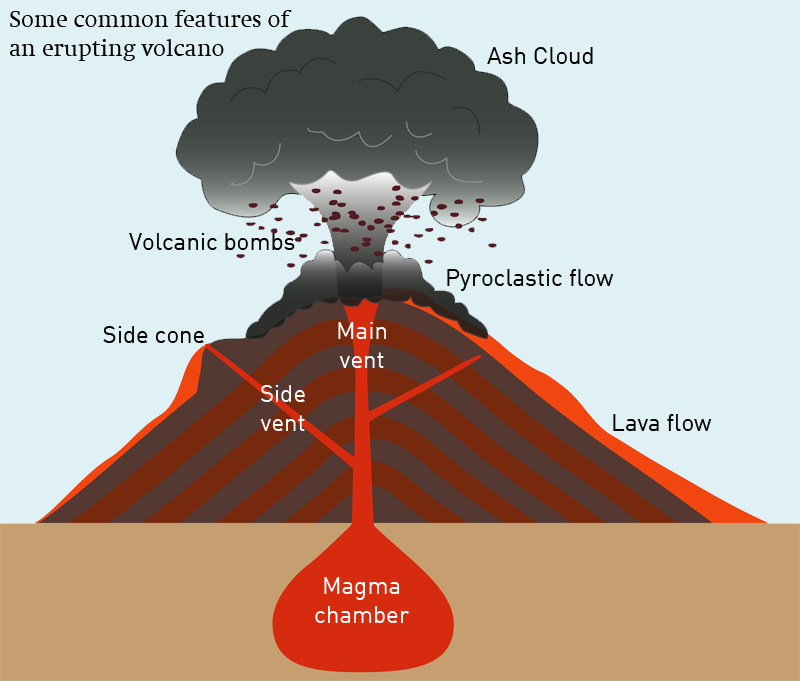
Anatomy of a Volcano All volcanoes have some things in common: Did you know? What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is molten rock stored in the Earth's crust. Lava is molten rock that has reached the Earth's surface through a volcanic vent. Where volcanoes are found The lithosphere is the outermost layer that surrounds the Earth.

Diagram Lava Dome Volcano Volcano Erupt
Anatomy of a Volcano What's the difference between lava and magma? What are volcanic vents, dikes, and fissures? In this anatomy of a volcano, explore the basic geological features of a.

The Amazing of the Volcano
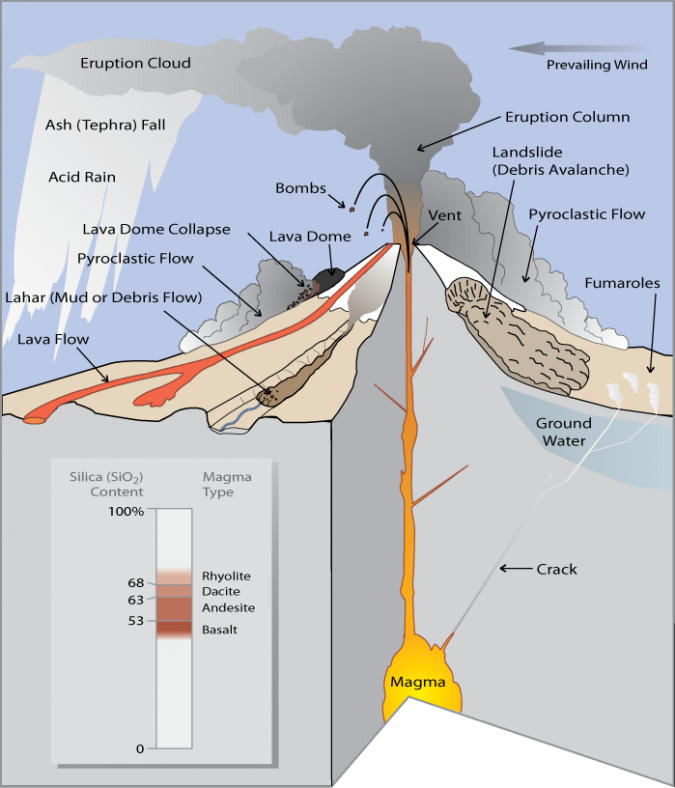
A collapsing column of ejected ash and gas from the Hunga volcano caused damaging submarine currents in 2022. In December 2021, an undersea volcano in the southern Pacific Ocean, the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai (hereafter called the Hunga volcano) began erupting. In January 2022 the eruption reached a powerful climax, triggering atmospheric.

Year 8 geography Anatomy of a volcano Diagram Quizlet
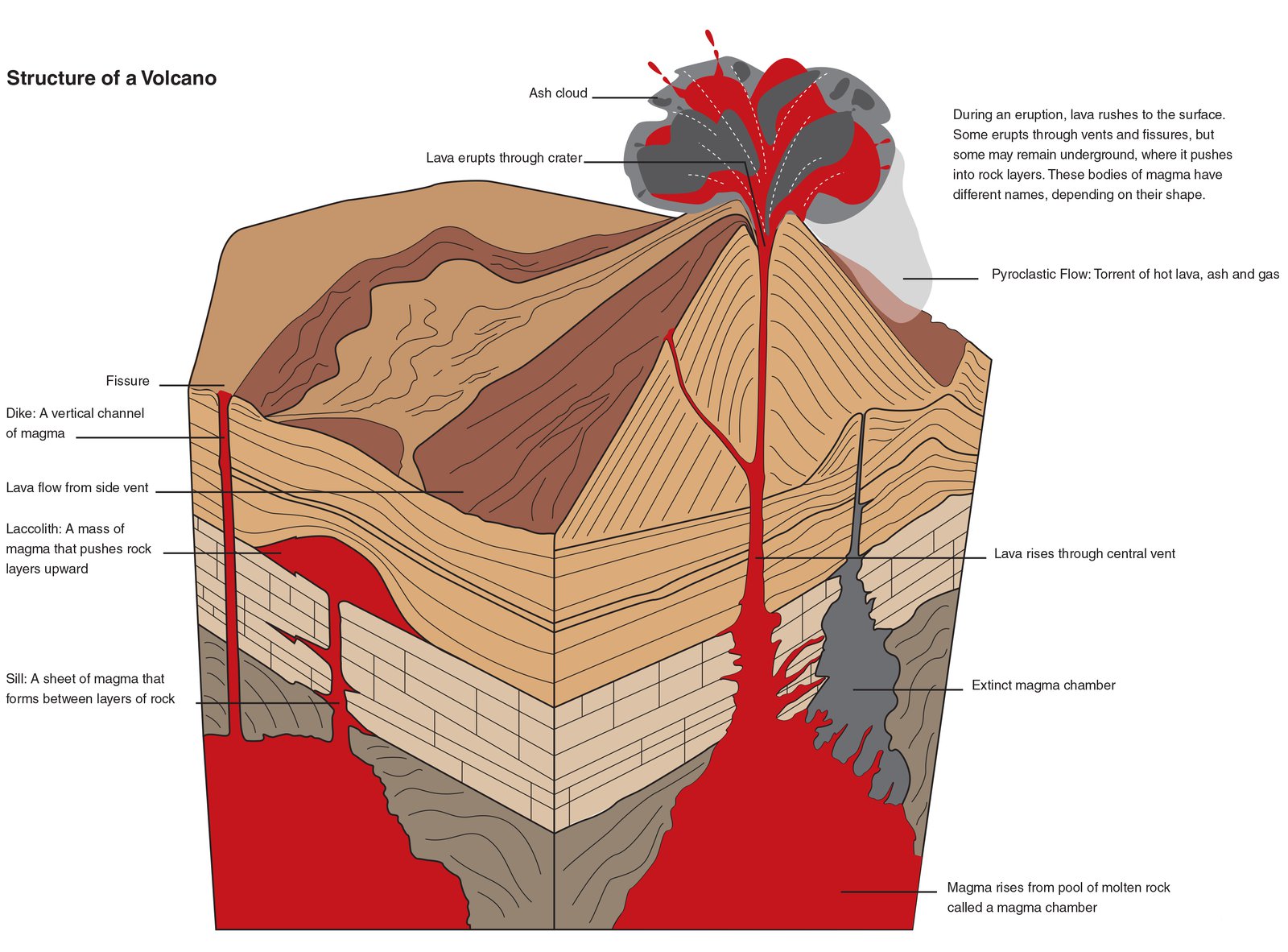
The structure of a volcano grows with every eruption. Below the surface, lava is called magma and builds up in underground reservoirs. Magma and other volcanic materials are channeled to the surface where they are expelled through a crack or hole. The main parts of a volcano include the magma chamber, conduits, vents, craters and slopes.
Structure of volcanoes The Australian Museum
Anatomy of a basaltic volcano July 14, 1993 Kilauea volcano, in Hawaii, may be the best understood basaltic volcano in the world. Magma rises from a depth of 80 km or more and resides temporarily in near-surface reservoirs: eruption begins when the crust above one of these reservoirs splits open in response to a pressure increase.

Volcano Eruption Diagram / Professor Garfield Download this free vector about diagram showing
But do you know the anatomy of a volcano? From tephra to volcanic bombs, it's time to explore the 13 parts of a volcano. Let's dive right in. 1. Magma When rocks become so hot, they can become a substance called magma. It collects in magma chambers on average 1 to 10 km below the surface.
Anatomy of a Volcano Display
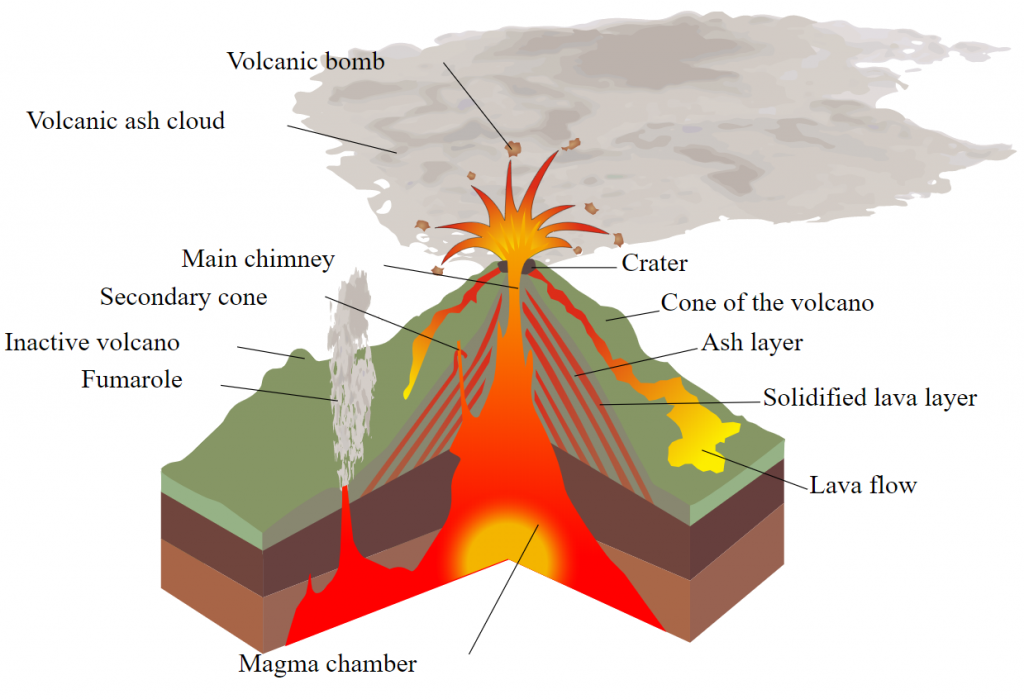
Introduction Volcanoes are both the vents where molten rock material and volcanic gases are erupted from within Earth's interior, and the cones and mountains built up around those vents. But beyond this simple definition, volcanoes are incredibly diverse with some types being very complex.
4.5 Volcanism Physical Geography and Natural Disasters
This magma surges through the surface of the earth, then solidifies, resulting over time in a classic volcano cone. — Lexi Krock Note: Some of the text in this feature is adapted from materials.

Volcanoes Infographic Science infographics, Volcano, Earth and space science
Craters and Other Volcanic Features reveals volcanoes' anatomy and describes major volcanic features found in national parks. Lava Flows and Other Volcanic Deposits describes the different types of lava flows and pyroclastic deposits as well as their characteristics and features.
13 Parts of a Volcano The Anatomy of Volcanoes Earth How
Volcano Anatomy. The main parts of a volcano are shown in Figure 11.4. When volcanoes erupt, magma moves upward from a magma chamber and into a vent or conduit. It flows out from a crater at the top, or sometimes emerges at a secondary site on the side of the volcano resulting in a flank eruption. Erupted materials accumulate around the vent.
Shetland's volcano Shetland Amenity Trust
volcano, vent in the crust of Earth or another planet or satellite, from which issue eruptions of molten rock, hot rock fragments, and hot gases. A volcanic eruption is an awesome display of Earth's power. Yet, while eruptions are spectacular to watch, they can cause disastrous loss of life and property, especially in densely populated.
Volcanoes 8th Grade Science with Mrs. Lewis
Here are the major parts: 1) Mantle From our tour of the Earth's interior, you'll remember that the mantle is the area of molten rock directly below the Earth's crust. This is where all the fun begins. Rock that is under intense heat and pressure circulates here. 2) Magma Chamber